PRESENT VERB TENSES AND IT'S USES
1. Present Simple Form
subject+v1/v3+object
The present tense is the base form of the verb:
I work in London.
But with the third person singular (she/he/it), we add an –s:
She works in London.
Present simple negatives
I like tennis but I don't like football. (don't = do not)
Angela doesn't drive to work. She goes by bus.
They don't work at the weekend.
John doesn't live in Manchester. (doesn't = does not)
USES OF PRESENT SIMPLE:
- For habits
He drinks tea at breakfast. - For repeated actions or events
We catch the bus every morning. - For general truths
Water freezes at zero degrees. - For instructions or directions
Open the packet and pour the contents into hot water. - For fixed arrangements
His mother arrives tomorrow.
Our holiday starts on the 26th March - With future constructions
She'll see you before she leaves.
2.Present Continuous Form
- Thing that are happening now
- Temporary events
- A new pattern or habit
- Future plans
When not to use!
It’s important to bear in mind that you cannot use the present continuous for all events taking place in the present. You do not use it to describe events that happen normally, or for a long time:
Eg: “I play the piano every morning” is correct.
“I am playing the piano every morning” is not correct, unless it was a new habit you had just started.
Another instance where you do not use the present continuous verb is with non-continuous verbs. These are a small group of verbs that describe things that you cannot normally see someone do, for example: to love, to fear, to want, to cost, and others. With these verbs, you use the present simple tense instead.
Eg. “A loaf of bread costs £1.50.”
You do not say “A loaf of bread is costing £1.50.”
3.Present Perfect Form
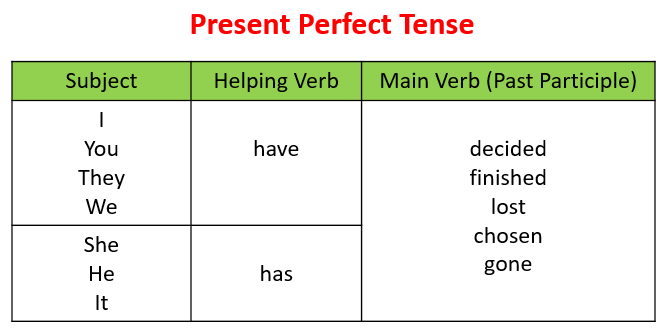
USES:
- Actions started in the past and continuing in the present
- When the time period referred to has not finished
- Actions repeated in an unspecified period between the past and now
- Actions completed in the very recent past (+just)
- When the precise time of the action is not important or not known
4.Present Perfect Continuous Form
We use the Present Perfect Continuous to talk about:
- past action recently-stopped
- past action still-continuing
Present Perfect Continuous for past action just stopped
We use the Present Perfect Continuous tense to talk about action that started in the past and stopped recently. There is usually a result now.
| I'm tired because I've been running. | |||||
| past | present | future | |||
| |||||
| Recent action | Result now | ||||
- I'm tired [now] because I've been running.
- Why is the grass wet [now]? Has it been raining?
- You don't understand [now] because you haven't been listening.
Present Perfect Continuous for past action continuing now
We use the Present Perfect Continuous tense to talk about action that started in the past and is continuing now. This is often used with for or since.
| I have been reading for 2 hours. | ||||
| past | present | future | ||
| Action started in past. | Action is continuing now. | |||
- I have been reading for 2 hours. (I am still reading now.)
- We've been studying since 9 o'clock. (We're still studying now.)
- How long have you been learning English? (You are still learning now.)
- We have not been smoking. (And we are not smoking now.)
For and Since with Present Perfect Continuous tense
We often use for and since with perfect tenses:
- We use for to talk about a period of time: three hours, two months, one decade
- We use since to talk about a point in past time: 9 o'clock, 1st January, Monday
| for | since |
| a period of time | a point in past time |
| - - - - - - - - - - - - | - • - - - - - - - - - - |
| 30 minutes | 10.00am |
| four days | Friday |
| 3 months | March |
| 2 years | 2010 |
| 3 centuries | 1700 |
| ages | I left school |
| ever | the beginning of time |
| etc | etc |
Look at these example sentences using for and since with the Present Perfect Continuous tense:
- I have been studying for three hours.
- I have been watching TV since 7pm.
- Tara hasn't been feeling well for two weeks.
- Tara hasn't been visiting us since March.
- He has been playing football for a long time.
- He has been living in Bangkok since he left school.





Comments
Post a Comment